What is PET scan (Positron Emission Tomography) & MRI Scan (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) Moreover, Indications, Preparation, Definition, etc?
What is a PET scan?
A PET scan is a diagnostic imaging technique in which parents are given a special radioactive substance that emits positrons; these, in turn, grow rise to gamma rays, which are detected by a gamma camera. It gives a three-dimensional image or picture of functional processes in the body.
Many different radioisotopes are useful in PET scanning. Such as Fluorine-18, Oxygen-15, and Carbon-11. 3F has commonly used isotopes. It replaces the hydroxyl (OH) group of molecules of interest. A PET scan demonstrates the biological functions of the body before anatomical changes take place, while the CT scan provides information about the body's anatomy such as size, shape, and location.
Indications
- To detect malignancy
- To diagnose Seizures/Epilepsy, Alzheimer's and other Dementias, Schizophrenia, Depression, Attention Deficit Disorder (ADD), and other neurologic disorder.
Equipment
- PET Camera
- Medical Cyclotron( for the production of Radioisotopes)
Preparation of the patient
- Explain the procedure to the patient
- The patient is asked to wear a gown during the exam
- Make sure that the patient is not pregnant
- 6 hours of fasting is required
- Explain to the patient that radio Isotopes has to be given intravenously half prior to the study.
- The patient is asked to lie down quietly for about 30 minutes after the injection. It is very important to stay as still as possible during this time.

PET scan
Post-Procedure care

- Inform the patient once the procedure is completed
- Help him; her to be oriented back to set up
- Make arrangements to send the patient back to the ward OPD. (specific points will be discussed under each system)
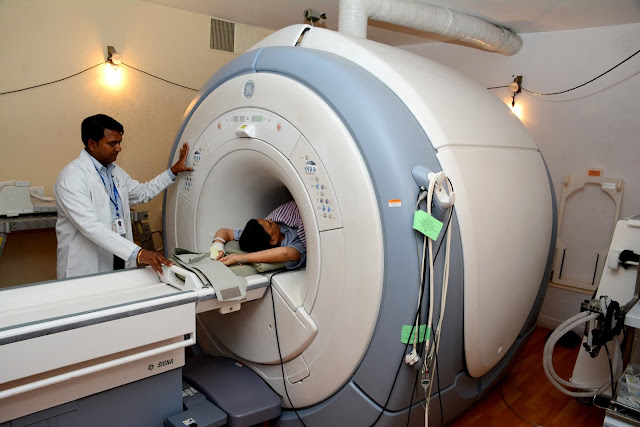
What is an MRI scan?
The full form of MRI (magnetic, Resonance Imaging), his technique of tomography-based upon the magnetic behavior of protonsespecially H+ in the body tissues when subjected to the magnetic field and RF pulses.
(NUCLEAR MAGNETIC RESONANCE IMAGING)
Indications of MRI scan
- Tumor of brain or meninges
- Skull base or orbital tumor
- Pituitary tumor
- Inflammation of the brain meninges
- Encephalopathy
- Encephalitis
- ENT problems- following consultation with a Radiologist
- The demyelinating disease of the brain
- Congenital problems
- Head trauma
- Epilepsy
- Stroke
- Post-operative follow-up after brain surgery
- Spinal cord compression (acute)
- Radiculopathy with neurological signs
- Trauma
- Tumour and infection arising in bone or other connective tissue
- Infections arising in bone or other connective tissue
Contra-Indications
Ferromagnetic implants (e.g.: Cardiac pacemakers, metallic orthopedic device, metal aneurysm dips, cardiac valve. for cardiac pacemaker and prosthetic valve, patients asked to get the card of the manufacturer along with him/her).
Equipment
- MRI machine
- RF coil
Preparation of the patient
- Explain the sequence of procedure
- Inform the patient that MRI is a painless procedure that does not require ionizing radiation and has no known risks
- Explain to the patient that he/she will lie flat on a narrow table inside the round opening of a large magnet and patient that he/she should lie motionless during the scan
- Tell him/her that they will hear a soft humming sound and on-off pulses of radiofrequency waves
Related Topics #sonography
3. Abnormal uterus.





Post a Comment